Dive deeper into Piping Tech’s thorough expansion joint cycle test as we show an actual demonstration of our expansion joint testing process.
Tag: expansion joint testing
How do you perform a burst test?
The burst test is primarily conducted on bellows. Normally, hydraulic pressure is slowly increased until failure occurs. Based on the burst test results, a safety factor is applied. This establishes the ultimate pressure rating.

Burst Testing
What is burst testing?
The objective of the burst test is to determine the ultimate pressure resistance. This test is primarily conducted on bellows. Normally, hydraulic pressure is slowly increased until failure occurs. Based on the burst test results, a safety factor is applied. This establishes the ultimate pressure rating.

Burst Testing
When cycle testing an expansion joint, what was the length of the stroke?
When cycle testing, the length of stroke is from neutral position to the compressed movement and back to neutral position of the expansion joint.
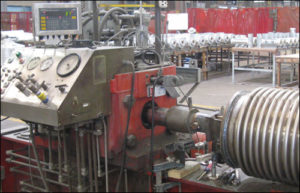
What acceptance criteria do you use for air testing the fabric expansion joints?
We do not air test fabric expansion joints; all welds are liquid penetrant tested.

Why should we do a dye-penetrant test?
Dye-penetrant tests should be performed in order to check the integrity of the welds. At U.S. Bellows, all bellows undergo a dye-penetrant examination before being shipped to the customer.

What are the quality tests that are conducted on expansion joints?
At U.S. Bellows, we perform a variety of tests:
- Burst Testing – The objective of the burst test is to determine the ultimate pressure resistance. Primarily conducted on bellows. Normally, hydraulic pressure is slowly increased until failure occurs.
- Dye Penetration Testing – Liquid dye is used to locate leaks or cracks in the bellows.
- Hydro Testing – Bellows are pressurized for 30 minutes to locate leaks or cracks.

Burst Testing
How do you service test an expansion joint?
Expansion joints are maintenance-free. They can only be tested if the expansion joint is supplied with 2-ply testable bellows using vacuum or air pressure testing.

How do you detect a crack in a fatigue testing machine?
Cracks on a fatigue testing machine are detected by the loss of internal pressure that is shown pressure gauge on the machine.

What is the difference between pneumatic testing and helium testing?
For pneumatic testing, air is used as the medium for testing and for helium testing they use helium, and the cost for helium is much higher.

How long is a burst test on an expansion joint?
A burst test is performed under controlled conditions and pressure is applied over a period of one to two hours using the necessary safety precautions for all personnel involved.

What is blotting in a dye-penetrant test?
Blotting on a dye-penetrant test typically indicates a crack in the weld. Therefore, the crack would be repaired and the test performed once again.



