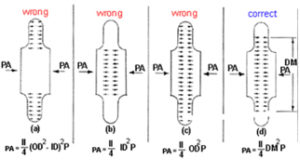
It is the force generated by the expansion joint due to the pressure inside. As shown in the picture, we have seen several incorrect ways to calculate the thrust force of an expansion joint. Per the EJMA Standards, as well as ASME Section VIII B&PV Codes, the Pressure thrust is calculated by multiplying the Bellows Effective Area, corresponding to the mean diameter of the convolutions of the Bellows by the Pressure of the line.
Read MoreTag: Expansion Joint Pressure
Why do bellows squirm under pressure?
What is the threshold pressure limitations of a fabric expansion joint?
| Fabric Expansion Joints can withstand up to 3 PSIG (pounds per square inch gauge) or 100″ of water (H₂O) column (In pressure). If the pressure exceeds this amount, it is best to use a metallic expansion joint. |
Does the expansion joint still work if the balancing side pressure is higher than the inline side?
The pressure is equal on both sides for a pressure balanced expansion joint. If the pressure difference is minor, it would not be a problem, but if the pressure thrust is high, then an imbalance of forces would occur and could result in forces being transmitted to adjacent equipment.
What is the pressure rating for an expansion joint?
The pressure rating is the maximum allowable pressure that the particular expansion joint can absorb. This is determined on a case-by-case basis.

What does pressure balance mean?
Pressure balance joints balance the pressure thrust forces inside of the expansion joint tie rods.

How do you attach a high pressure joint in a piping system?
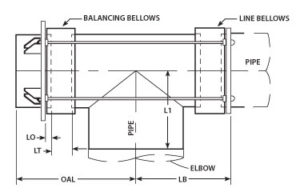
In an axial piping system, the expansion joint should be located as close as possible to a main anchor. The first pipe guide should be located at a distance of 4 pipe diameters away from the expansion joint. The second guide should be located a distance of 14 pipe diameters away from the first guide. During installation, the expansion joint should be either welded or flanged into the piping system.

If a simple bellows is designed without limit rods (for operating cases), under a hydro test, do you recommend adding limit rods?
Yes, if they are testing just the expansion joint or if they are testing when installed, they have to make sure that the pipe line is anchored or have limit rods added to the expansion joint to absorb the pressure thrust.

What is the highest pressure that an expansion joint can take?
The pressure rating an expansion joint can take depends upon pipe size and temperature. Standard units from 3 inches to 24 inches are suitable for 300 PSIG. (pounds per square inch) Higher pressures can be accommodated on a case by case basis.

Where does the pressure thrust act in a single bellows turbine exhaust application?
If the expansion joint is not tied the pressure thrust will act on the turbine exhaust nozzle and the adjacent piping.
What are the pressure ratings specified in expansion bellows?
The pressure rating is the maximum allowable pressure to be used for that particular expansion joint. Each pressure rating is specified on a case-by-case basis per expansion joint.

What is squirm pressure?
Squirm pressure is the pressure at which in-plane instability occurs.

How do define a hydro-test pressure based on design pressure?

How does US Bellows define a hydro-test pressure based on design pressure?
When determining the pressure for hydrostatic testing of your expansion joints, the most important aspect is the applicable design codes. Normally, the ASME SEC VIII Div.1 general hydro-test pressure will be 1.3 x design pressure, but if you are testing for ASME B31.1, B31.3,B31.4, it will be 1.5 x design pressure.
That being said, there are many other considerations that will determine the test pressure, such as:
- Test Duration
- Temperature
- End conditions of the assemblies
- Special cases based on the customer’s situation
Be sure to discuss with our engineers so that we can correctly test your bellows and expansion joints.
How do you calculate pressure thrust load?
| Pressure thrust load is calculated by finding the area of the mean diameter of the bellows and multiplying it by the design pressure. |