It is recommended that all expansion joints include liners in order to protect the bellows from the internal flow environment.

It is recommended that all expansion joints include liners in order to protect the bellows from the internal flow environment.

It is recommended that all expansion joints include liners in order to protect the bellows from the internal flow environment.

A movement guide controls the thermal motion of the piping system into the bellows
A movement guide controls the thermal motion of the piping system into the bellows
Read MoreExpansion couplings are used mainly to connect two pieces of pipe together.
Usually, the liner material can be the same as the system pipe material, such as carbon steel, with liner thicknesses of 1/8-inch and greater depending upon flow rate and diameter.

Usually, the liner material can be the same as the system pipe material, such as carbon steel, with liner thicknesses of 1/8-inch and greater depending upon flow rate and diameter.

The growth of an expansion joint bellows is restrained with the use of limit rods.

The growth of an expansion joint bellows is restrained with the use of limit rods.

Internal liners are an expansion joint accessory used to protect the convolutions from direct flow impingement, which can cause erosion and flow-induced vibration. They are recommended to extend the life of metallic expansion joints.

Internal liners are an expansion joint accessory used to protect the convolutions from direct flow impingement, which can cause erosion and flow-induced vibration. They are recommended to extend the life of metallic expansion joints.

Yes for a simple bellow, the tie-rods main purpose is to hold the pressure thrust.

Pressure thrust can be absorbed by placing anchors in a system or by using an expansion joint with tie rods.
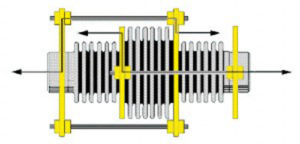
Pressure thrust can be absorbed by placing anchors in a system or by using an expansion joint with tie rods.

A directional anchor restrains the pressure thrust from the expansion joint and allows for movement in a direction perpendicular to the pressure thrust.

A directional anchor restrains the pressure thrust from the expansion joint and allows for movement in a direction perpendicular to the pressure thrust.

The tie rods are used to take the pressure thrust forces. Most universal expansion joints use tie rods to eliminate the requirements for main anchors
The tie rods are used to take the pressure thrust forces. Most universal expansion joints use tie rods to eliminate the requirements for main anchors
Read MorePantographic linkage is an accessory that is used to distribute axial movement between two bellows, allow lateral motion and support the weight of the center pipe section between the bellows.

The number of tie-rods used is determined by the design pressure of the expansion joint. It can range from two to eight tie rods in extremely high-pressure conditions.
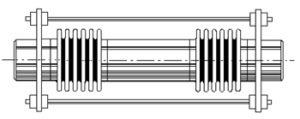
Control rods are used to control axial and lateral movements of the expansion joint.

Control rods are used to control axial and lateral movements of the expansion joint.What is the purpose of the control rods in an expansion joint?

Limit rods are used to limit axial expansion or compression to prevent the bellows from over-compression. Limit rods are designed to absorb the pressure thrust of the expansion joint in case of anchor failure.

Limit rods are used to limit axial expansion or compression to prevent the bellows from over-compression. Limit rods are designed to absorb the pressure thrust of the expansion joint in case of anchor failure.

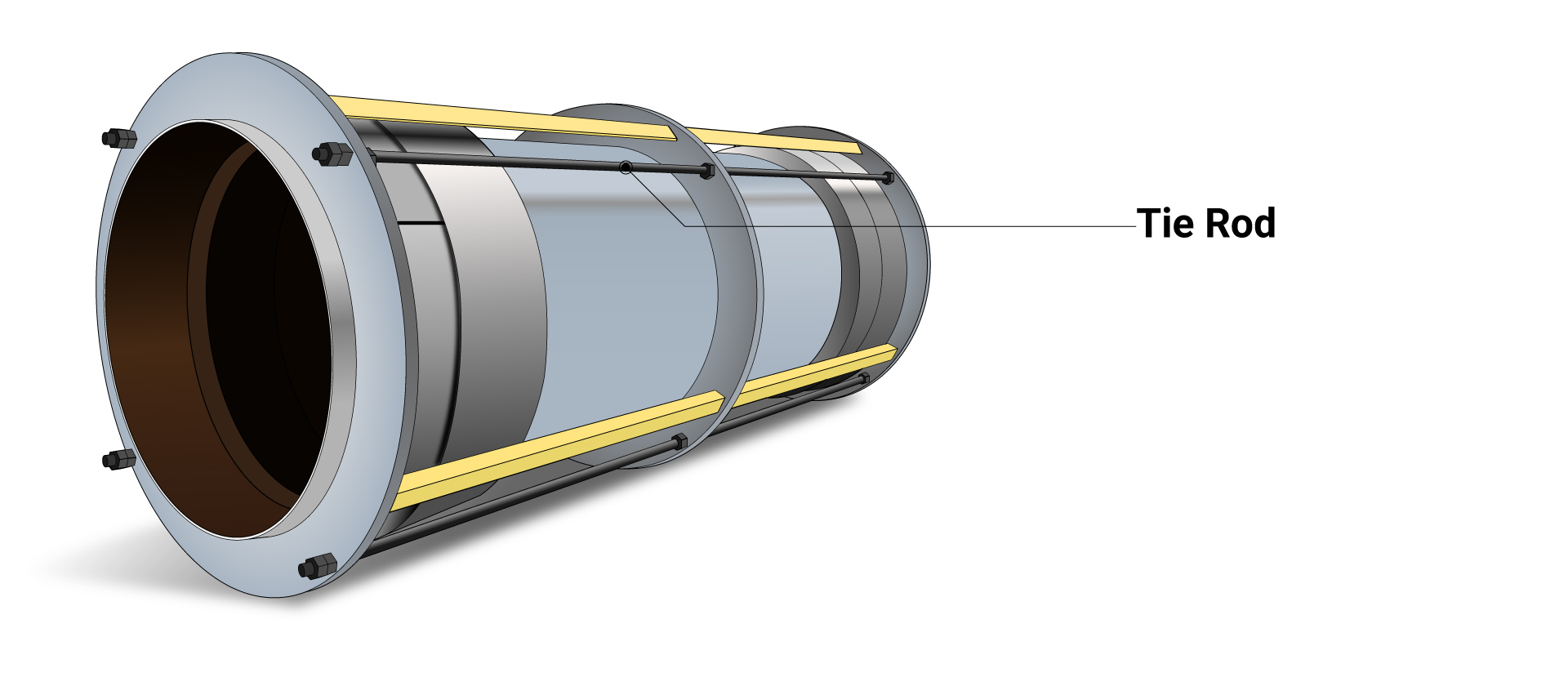
Tie rods are vital components of expansion joints. Their job is to maintain full pressure thrust from the bellows and the pipeline. This prevents the pressure force of the pipeline from pushing and over-stressing the piping system anchors or equipment.
Tie rods help restrain this force. They allow the expansion joint to move side-to-side without requiring large, expensive main anchors.
Tie rods are engineered to manage the significant internal pressure forces within a piping system. By connecting the ends of the expansion joint, they create a continuous support.
This absorbs the pressure thrust and, at the same time, prevents the bellows from overextending. This delivers the required flexibility in the system and protects the surrounding equipment and pipe supports from damaging forces.
The only forces that the piping system would need to worry about are the spring rate forces of the expansion joint, i.e, the force required to move the expansion joint laterally.
Note that you must use two tie rods for angular rotation to happen. You should place these rods at a 90-degree angle opposite the direction of rotation.
Tie rods restrain pressure thrust while allowing for lateral deflection, which is crucial for piping systems that experience lateral movement.
There’s also another important aspect to consider: the economic advantage of using tie-rods on an expansion joint. As explained previously, adding tie-rods to an expansion joint restrains the pressure thrust of the pipe. This allows the piping designer to eliminate bulky anchors that are overdesigned to handle the full pressure load, and may eliminate many guides since the tied expansion joint is self-supporting.
While the upfront cost of a tied universal expansion joint is higher compared to a single expansion joint, you need to consider the cumulative costs of guides that would be needed in the single expansion joints to prevent them from buckling, plus the anchors for the pipe ends. Those additions make single expansion joints the more costly choice.
Not sure about whether your expansion joint needs tie rods or how adding tie rods could affect your piping system? Schedule time with our engineers or download a catalog.
Next read: The difference between tie rods and limit rods.

Tie rods are vital components of expansion joints. Their job is to maintain full pressure thrust from the bellows and the pipeline. This prevents the pressure force of the pipeline from pushing and over-stressing the piping system anchors or equipment.
Tie rods help restrain this force. They allow the expansion joint to move side-to-side without requiring large, expensive main anchors.
Tie rods are engineered to manage the significant internal pressure forces within a piping system. By connecting the ends of the expansion joint, they create a continuous support.
This absorbs the pressure thrust and, at the same time, prevents the bellows from overextending. This delivers the required flexibility in the system and protects the surrounding equipment and pipe supports from damaging forces.
The only forces that the piping system would need to worry about are the spring rate forces of the expansion joint, i.e, the force required to move the expansion joint laterally.
Note that you must use two tie rods for angular rotation to happen. You should place these rods at a 90-degree angle opposite the direction of rotation.
Tie rods restrain pressure thrust while allowing for lateral deflection, which is crucial for piping systems that experience lateral movement.
There’s also another important aspect to consider: the economic advantage of using tie-rods on an expansion joint. As explained previously, adding tie-rods to an expansion joint restrains the pressure thrust of the pipe. This allows the piping designer to eliminate bulky anchors that are overdesigned to handle the full pressure load, and may eliminate many guides since the tied expansion joint is self-supporting.
While the upfront cost of a tied universal expansion joint is higher compared to a single expansion joint, you need to consider the cumulative costs of guides that would be needed in the single expansion joints to prevent them from buckling, plus the anchors for the pipe ends. Those additions make single expansion joints the more costly choice.
Not sure about whether your expansion joint needs tie rods or how adding tie rods could affect your piping system? Schedule time with our engineers or download a catalog.
Next read: The difference between tie rods and limit rods.
Read More