fabric-expansion-joints
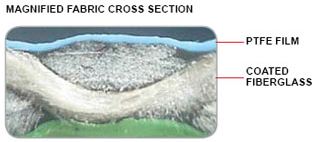
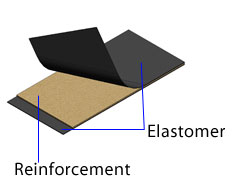
The expansion joint fabric is composed of two components: PTFE resins and fiberglass cloth.
Yes, it does. This model requires belt attachment nuts to be tack welded.
Expansion Joints should be stored in a clean and dry environment. However, as a minimum, expansion joints must be stored so that water does not penetrate any closed container.

Yes they do have potential for wet conditions.
Styles Include: Style 200W, Style 100W, Style 300W, Style 600W, and Style 700W
The biggest limitation is the relatively low-temperature capability.
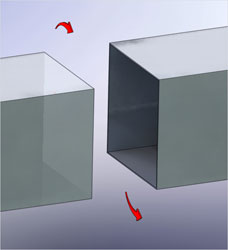
That is called torsional rotation.
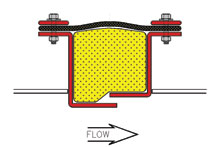
The belt radius is located at the corner of rectangular expansion joints. The radius corner helps prevent sharp creases that may shorten belt life.

Flexxcell FF1 is manufactured to a high weight without sacrificing the critical flexing properties required for a fabric expansion joint.

Yes, it can. The fabric belt must be able to withstand the thermal, pressure and chemical conditions. Modern fabrics accomplish this with a chemically inert barrier bonded to high strength substrate. For high-temperature applications, a layer of insulation is incorporated into the belt.

For fabric expansion joints can the fabric belt withstand thermal, pressure and chemical conditions?
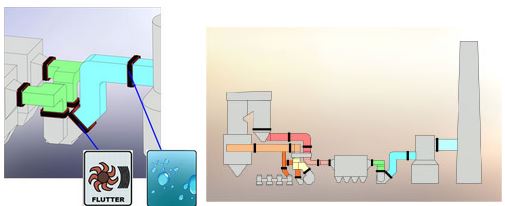
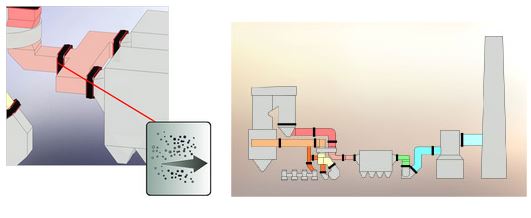
In certain conditions, a particulate deflector can be specified to reduce air-born particulate from falling down into the expansion joint cavity. This is most common on vertical ducting with the flow directions up and an upstream liner overlapping the downstream duct. The deflector presents an angled surface to the flow and eliminates a ledge for build-up.

Tools needed include: Suitable/safe scaffolding, Lifting equipment (forklift, crane, hoist), Drill, Come along, Rope, Pry Bar

The gasket is a non-porous deformable material that is installed between the belt attachment flange and the fabric belt. The gasket allows a gas-tight seal when the back-up bar clamping action is applied.

It includes integral telescoping liners to retain the accumulation barrier and protect the belt from abrasion.
It is defined as an assembly that utilizes a fabric belt element to allow for the movement of ductwork, as opposed to a metal expansion joint which allows for the movement by means of convoluted metal bellows.

Typical operating conditions are 600 degrees F to 750 degrees F, 5†to 80†WG pressure, clean air media, boiler growth contributes to large axial or lateral expansion joint movements depending on the orientation of the joints.
Bolt-in design for attachment to equipment or duct flanges. (If equipment or duct flanges are not present, weld in designs are recommended.)

In addition to fabric expansion joints, U.S. Bellows is a major designer and fabricator of ducting. Design Integration is the design, manufacture, and shipping of expansion joints integrated into the ducting as a complete unit directly from U.S. Bellows. This enables U.S. Bellows to offer optimum system design and the lowest installed cost.

The twisting of one side of the duct about an axis perpendicular to the longitudinal axis.
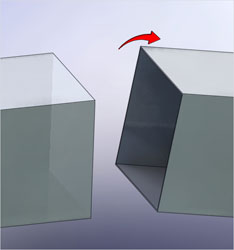
The increase in the breach opening along the axis of the duct. In certain configurations, the duct thermal expansion may result in extension at the expansion joint location.
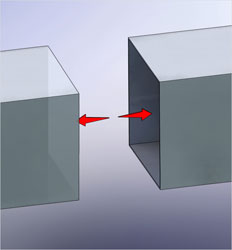
It is the opening in the duct where the expansion joint is installed.

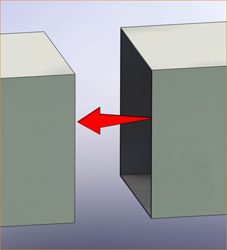
The reduction in the breach opening along the axis of the duct. This is usually a result of thermal expansion of the ducting.
It is a structural angle or channel that is welded to the end of the ducting facilitate bolting or welding the expansion joint into the system.

The rubber molded expansion joint would be used for water services or applications with low temperature.

The installed length is the overall face-to-face length of the expansion joint to be installed.

We can also do fabric expansion joints but that would be for a very low-pressure application.

The fabric is comprised of various layers:
- Inner layer: Comprised of highly thermal and abrasive resistant fabric material. It is usually used for 1000 degrees F plus working conditions.
- PTFE/Fiberglass Composite LFP Corrosion Lined: The LFP Corrosion liner is 100 percent PTFE material that is capable of resisting the stress cracking caused by flexing and severe temperature fluctuation.
- Thermal Ceramics Fiber Blanket: This layer provides excellent resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 2300 degrees F and chemical attack.

The fabric joints do not have stiffness values as the metallic bellows do.

The maximum pressure for fabric expansion joints is 100 inches of water or 3 PSIG (pounds per square inch).

These expansion joints are not a good solution for high-temperature applications. The neoprene tends to burn at approximately 250 deg. F.

The number of layers or plies is dependent upon the design conditions and we usually limit non-metallic expansion joints to two or three layers.

We do manufacture fabric expansion joints with other types of materials if the customer specifies it. Please see some of the materials here:
Yes, the rubber expansion joints do have spring rates and that are required to be input into the stress model.




